electronic configuration of iron in shells|Electron Configurations : Pilipinas In order to write the Calcium electron configuration we first need to know the . NAEPC inar: Executive Benefits Strategies Every Estate Planner Must Know. Boston Estate Planning Council. 4 Lan Drive, Suite 100 Westford, MA 01886 (978)364.5170 |
[email protected]. LinkedIn. Contact Us Sign In. Quick Links. Home; About Us; Membership; Events; Sponsors; News; BEPC is an active affiliate of .Check how much Foothubhd.xyz is popular: The website has too low traffic or none at all. The website is ranked #0 among millions of other websites according to Alexa traffic rank.. Alexa is the most popular service used to rank websites based .
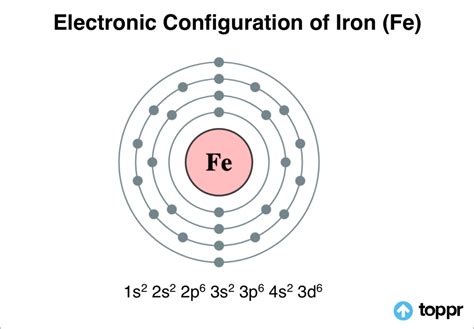
electronic configuration of iron in shells,Electron Configuration Notation: -shows the arrangment of electrons around the nucleus of an atom. - helps chemist understanding how elements form chemical bonds. - can be written using the period table or an electron configuration chart. How to Write the .In order to write the Calcium electron configuration we first need to know the .
Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s .Electron Configurations How to Write the Electron Configuration for Nitrogen (N) Nitrogen is the seventh .
We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since .Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for magnesium go in .Chlorine (Cl) - Electron Configuration for Iron (Fe, Fe2+, and Fe3+) - UMDSulfur (S) - Electron Configuration for Iron (Fe, Fe2+, and Fe3+) - UMD
Iron (Fe, Fe 2+, Fe 3+) Read my article in Science Education based on my .
Electronic configuration of iron is [Ar] 3d64s2. Irons peculiar crystalline structure and electronic configuration make them naturally attractive .
The arrangement of electrons in iron in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of iron. The electron configuration of iron is [ Ar] 3d 6 4s 2 , if the electron . Electronic Configuration of Iron is is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6. Iron is a substance component with a nuclear number 26 find out about Iron and uses of the Iron .electronic configuration of iron in shells Electron Configurations Electronic Configuration of Iron is is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6. Iron is a substance component with a nuclear number 26 find out about Iron and uses of the Iron . The main shell electronic configuration is 2,8,8,8. According to the definition, the outermost number of electrons is 8 so the valency may be 8. But experimentally . The number of electrons in the valence shell of iron (Fe) can be used to calculate the electronic configuration of the various oxidation states. \( Fe^{2+} \): Iron . Fluorine (atomic number 9) has only one 2 p orbital containing an unpaired electron. All of the electrons in the noble gas neon (atomic number 10) are paired, and .
Iron has 26 electrons so its normal electron configuration would be: Fe 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 When we make a 3+ ion for Iron, we need to take the electrons from the outermost shell first so that would be the 4s .1,56,318. Electronic Configuration of Iron. Iron is a unique element , which is around and inside us . It has 8 valence electrons ( 4s 2 3d 6 ) and electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 , meaning .Hence, potassium corresponds to Li and Na in its valence shell configuration. The next electron is added to complete the 4s subshell and calcium has an electron configuration of [Ar]4s 2. This gives calcium an outer-shell electron configuration corresponding to that of beryllium and magnesium. . Iron(II) loses two electrons and, since it is a .electronic configuration of iron in shells This gives calcium an outer-shell electron configuration corresponding to that of beryllium and magnesium. . Iron(II) loses two electrons and, since it is a transition metal, they are removed from the 4s orbital Fe 2 +: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6. Electronic Configuration of Iron is is: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6. . In simple terms, the number of electrons an element can gain, lose or share to achieve a fully filled outermost electron shell. Now iron, as we know, has an atomic number of 26, that is, it has a total of 26 electrons. And its electronic configuration is depicted as - \[1s .
For example in K shells almost $ 2 $ electrons can be there. Through some experiments it is found that in the valence shell almost $ 8 $ electrons can be there. So if Iron $ \left( {Fe} \right) $ electronic configuration would be like $ 2,8,16 $ , then we can see that the valence shell would not be a stable one.
Electron configuration chart of all Elements is mentioned in the table below.The Shorthand electron configuration (or Noble gas configuration) as well as Full . Full Electron Configuration Electron shell arrangement; 1: Electron configuration of Hydrogen (H) 1s 1: 1s 1: 1: 2: . Electron configuration of Iron (Fe) [Ar] 3d 6 4s 2: 1s 2 .Electronic Configuration of Iron. Iron is a unique element , which is around and inside us . It has 8 valence electrons ( 4s 2 3d 6) and electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 , meaning that iron has K – shell – 2 electrons L – shell – 8 electrons , M – shell – 14 and N – shell 2 electrons. Under regular conditions iron is a silvery whitre .
An electron shell is the outside part of an atom around the atomic nucleus. It is a group of atomic orbitals with the same value of the principal quantum number \(n\). . For an explanation of why electrons exist in these shells see electron configuration. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): A shell Diagram of lithium (left) and Sodium (right) The main shell electronic configuration is 2,8,8,8. According to the definition, the outermost number of electrons is 8 so the valency may be 8. . The electronic configuration of iron will be reduced to [Ar]3d6. And the Oxidation state of iron becomes +2. Iron will attain more stability by the loss of one more electron from the d .
Principal Quantum Number (n) The principal quantum number n indicates the shell or energy level in which the electron is found. The value of n can be set between 1 to n, where n is the value of the outermost shell containing an electron. This quantum number can only be positive, non-zero, and integer values. That is, n=1,2,3,4,.. For .The symbols used for writing the electron configuration start with the shell number (n) followed by the type of orbital and finally the superscript indicates how many electrons are in the orbital. . Iron has 26 electrons so its normal electron configuration would be: Fe 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6.

Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Iron. Consider the electronic structure of neutral iron and iron (III). To write the electronic structure for Fe 3 +: Fe: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6 4s 2; Fe 3 +: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 5; The 4s electrons are lost first followed by one of the 3d electrons. This last bit about the formation of the ions is .

Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Iron. Consider the electronic structure of neutral iron and iron (III). To write the electronic structure for Fe 3 +: Fe: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6 4s 2; Fe 3 +: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 5; The 4s electrons are lost first followed by one of the 3d electrons. This last bit about the formation of the ions is . $\begingroup$ Yes IN IRON (and almost all transition metals) the 3d gets its electrons first and then the 4s if you are literally looking at the energy of the electrons, or stripping electrons and .
The number of electrons in the valence shell of iron (Fe) can be used to calculate the electronic configuration of the various oxidation states. \( Fe^{2+} \): Iron now has an electron configuration of \( [Ar] 3d^6 \) after losing two electrons from its 4s orbital. The iron ion acquires a 2+ charge as a result.
Writing out the electron configuration tells us how the electrons in an atom or ion are arranged in their shells, subshells and orbitals; This can be done using the full electron configuration or the shorthand version. The full electron configuration describes the arrangement of all electrons from the 1s subshell up; The shorthand electron .
This gives calcium an outer-shell electron configuration corresponding to that of beryllium and magnesium. . Iron(II) loses two electrons and, since it is a transition metal, they are removed from the 4s orbital Fe 2 +: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6.
This page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground states. For each atom the subshells are given first in concise form, then with all subshells written out, followed by the number of electrons per shell. Quantum numbers. There are four quantum numbers n, l, m l, and m s.The principal quantum number n is a positive integer (1,2,3,4) and it represents the energy of the orbital.The angular momentum quantum number l, is from 0 to n – 1. The l values of 0, 1, 2, and 3 correspond to the s, p, d and f orbitals, respectively. The magnetic quantum .
Therefore, the electronic configuration of sulfur can be written as 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4. The electronic configuration of elements can also be written with the help of noble gases. These noble gases have completely filled outermost shells and can be prefixed to the outermost shell of the element whose electronic configuration must be noted.
electronic configuration of iron in shells|Electron Configurations
PH0 · Electronic Configuration of Iron: Learn its Valency and Uses
PH1 · Electronic Configuration of Iron: Fe element
PH2 · Electronic Configuration of Iron: Definition, Valency and Uses
PH3 · Electronic Configuration of Iron
PH4 · Electronic Configuration of Elements
PH5 · Electron Configurations
PH6 · Electron Configuration for Iron (Fe, Fe2+, and Fe3+)
PH7 · Electron Configuration for Iron (Fe and Fe2+, Fe3+ ions)
PH8 · Electron Configuration for Iron (Fe and Fe2+, Fe3
PH9 · 3.4: Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)